Nowadays the use of refrigerators is enormous. The invention of the
refrigerator is the greatest milestone in human history ever. Without a
refrigerator, we cannot keep food fresh for a longer time, diseases spread
faster and even it also affects many industries like the Food industry,
ice plants, chemical plants, rubber industries, Pharmaceutical industries,
etc... Likewise, we can say much application of refrigeration.
Now we understood the importance of the refrigerator in our day-to-day
life. Does anyone know how a refrigerator works? We all know that
refrigerator is some sort of a cooling box inside which we place our food
products. Sometimes we also used to stand in front of the refrigerator in
summer days and also peeking through a partially closed refrigerator door
to check lights on or off LOL! Comment your funny experience with the
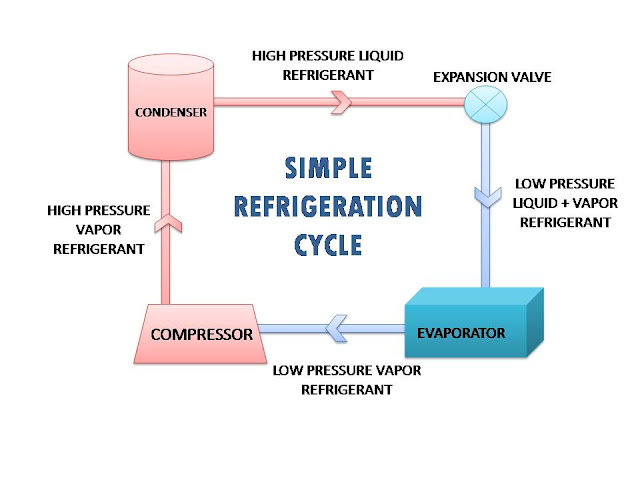
refrigerator. Let’s switch back to our topic. Refrigerators works on a simple process in which evaporation of refrigerant takes place in the
evaporator, during evaporation refrigerant absorbs heat around the
refrigerating space thus produces a cooling effect. Nowadays most of the refrigerators work on vapor compression refrigeration systems because of
their higher efficiency and ability to remove a large amount of heat with
less mass of flow of refrigerant. The four basic components of a
refrigerator are
-
Compressor
-
Condenser
-
Expansion device or metering device
-
Evaporator
Compressor:
By its name, we can understand that its function is to compress something. A compressor is an electrically driven pump used to increase the pressure of the fluid. In the refrigerator, compressor is used to compress liquid refrigerant to high pressure and circulates it again and again in cycles also it adds up the heat to the refrigerant. Without a compressor, the removal of heat takes place gets slower and the required cooling effect will not obtain in the required time. Thus compressor is like the heart of the refrigerator.
Compressor types:
1.
Reciprocating compressors
o
Open type reciprocating compressor.
o
Closed type reciprocating compressor or hermetically sealed
compressor.
o
Semi-Hermetically sealed compressor.
2.
Rotary compressors
o
Rolling piston-type rotary compressor.
o
Rotating vane-type rotary compressor.
o
Rotary screw compressor
3.
Centrifugal compressor
Condenser:
A condenser is a device that acts as a heat exchanger in the refrigeration system. It consists of steel or copper tubing through which the refrigerant flows. The size of the tube ranges from 6mm to 18mm. The high-pressure high-temperature vapor refrigerant from the compressor flows through the condenser in which the refrigerant rejects the heat energy gained in the evaporator and compressor.
Atmospheric air and water are the two most convenient heat sinks to which
heat can be rejected.
The condenser is broadly classified on the basis of the cooling medium
used:
1.
Air-cooled condensers
o
Natural convection air-cooled condensers.
o
Forced convection air-cooled condensers.
2.
Water-cooled condensers
o
Shell and tube condensers.
o
Shell and coil condensers.
o
Double tube or tube-in-tube condensers.
3.
Evaporative condenser
Expansion devices:
An expansion device is also known as a metering device or
throttling device. The expansion devices used with dry expansion
evaporators are usually called expansion valves.
Purpose of expansion devices:
Expanding the liquid refrigerant from the condenser pressure to the
evaporator pressure. To maintain a pressure difference.
To control the flow of liquid refrigerant according to the load on the
evaporator. While restricting the flow, also reduces the pressure of the
liquid refrigerant with the result the liquid change into a vapor of low
dryness fraction.
Types of expansion devices:
Some expansion devices used in industrial and commercial refrigeration
and air conditioning are
1.
Capillary tube,
2.
Hand-operated expansion value,
3. Automatic or constant pressure expansion value,
4.
Thermostatic expansion valve,
5.
Low side float value and
6.
High side float value.
Evaporators:
An evaporator is a device that absorbs heat from its surroundings or
space to be cooled or products to be cooled using a refrigerant. The
temperature of the boiling refrigerant in the evaporator must always be
less than that of the surrounding medium so that the heat flows to the
refrigerant and the evaporator becomes cold. The evaporator is installed on
the low-pressure side of the refrigeration system. The evaporator is also
known as a cooling coil, a chilling coil, or a freezing coil. The heat
absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator is carried by it to the
compressor. Then it goes to the condenser where the heat is taken out of
the refrigerant.
Classification of evaporators
|
S.n |
Criterion |
Types of evaporator |
|
1 |
Refrigerant feed |
Flooded type, dry or direct-expansion type, liquid overfeed
type. |
|
2 |
Surface construction |
Bare tube evaporators plate surface type, finned-tube
evaporator. |
|
3 |
Cooling medium |
Primary air cooling type
|
|
4 |
Operating medium |
Frosting type, defrosting type, non-frosting type |
|
5 |
Special design |
Walk in coolers, liquid chillers
|
Here are some other important parts of the refrigerator
Thermostat:
The control element which is used for measuring the temperature is known as a thermostat. When the desired temperature reaches inside the refrigerator the thermostat cuts off the electricity flowing through the compressor. So that the temperature is constantly maintained inside the refrigerator.
Various types of thermostats are available. They are
-
Bimetal type thermostat
-
Sealed bellow type/fluid-filled bulb type/immersion/remote
thermostat.
-
Electric resistance thermostat
- Thermocouple type thermostat
Insulation casing:
Insulation casing plays an important in the refrigerator. Without proper insulation, the desired cooling effect will not be maintained inside the refrigerator and also it increases the work of the compressor which leads to more consumption of electricity. So to avoid these problems proper insulation should be done in the refrigerator. Polyurethane(PU) foam is the most widely used insulation material for refrigerators. Its lesser heat loss and higher durability makes it a popular insulation material.
Defrost coil:
In the freezer, we can sometimes see a larger amount of ice formation takes place. This can be annoying right. To overcome the ice buildup inside the freezer, a defrost coil is placed within the evaporator coil. So whenever the ice buildup takes place the electricity to the compressor is stopped instead it flows through defrosting coil. The defrost coils get heated and melts the ice buildup and the water is drained in the drain pipe.
Don't forget to comment your funny experience with the refrigerator.